Mohamed, F., R. A. Zaghlool, and W. El Hotaby. "Terahertz spectroscopic analysis of non-radiated and radiated synthetic and natural polymer/GO nanocomposites." Journal of Molecular Structure (2021): 131659.
Abstract
Absorption coefficient, refractive index, and dielectric parameters of two sets of polymers: synthetic polymers (poly acrylamide, and poly vinyl alcohol), and natural polymers (chitosan, and cellulose acetate) have been investigated using Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy THz-TDS in the frequency range of 0.3 THz - 3.0 THz. It is found that these parameters are significantly boosted by the presence of graphene oxide (GO) as a filler. The influence of electron beam radiation of a dose of 50 kGy on the absorption coefficient, and refractive index is also investigated. An observable decrease in these parameters is illustrated in the un-doped and doped membranes upon irradiation. By this study, we shed light on how the THz-TDS is able to identify any variant change in the structure due to incorporation of GO or as an influence of electron beam radiation.
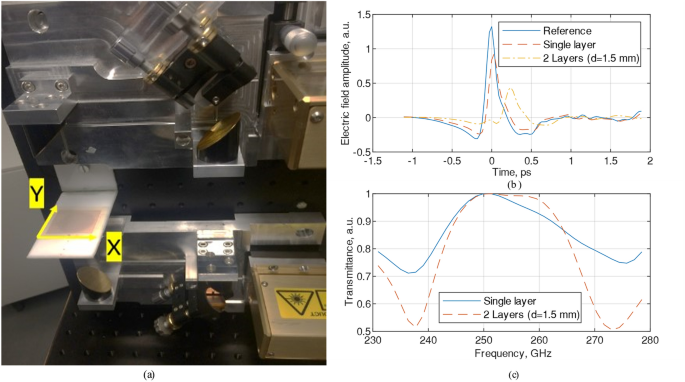
… atmosphere. 2.2.4. THz time- domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS).
The terahertz spectrometer in the frequency range of 0.3 THz and 3 THz (10 cm −1 -100 cm −1
), TPS spectra 3000 system, TeraView Ltd England, was used.
To …
for more information click here