for full paper see https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00339-022-06148-x
Monday, 14 November 2022
Structure-terahertz property relationship in tellurite glasses
for full paper see https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00339-022-06148-x
Friday, 11 November 2022
New TeraSolve system from TeraView for the analysis of the porosity of Solid dosage forms
Thursday, 10 November 2022
Soft Defect Localization and Characterization for Advanced IC Packaging Using Novel EOTPR In-Situ Dynamic Temperature Probing
Ko, Zhi Hao, Tom White, Jesse Alton, and Martin Igarashi. "Soft Defect Localization and Characterization for Advanced IC Packaging Using Novel EOTPR In-Situ Dynamic Temperature Probing." In ISTFA 2022, pp. 289-293. ASM International, 2022.
The high temperatures and thermal cycling experienced by integrated circuit packages can induce warpage that in turn can lead to cracks developing at material interfaces that compromise the integrity of electrical traces within the device. In this study, the authors demonstrate how Electro-Optical Terahertz Pulsed Reflectometry (EOTPR) with dynamic temperature control can be used to localize and characterize the resistive faults created by such thermally induced cracks. The EOTPR technique provides quick, reliable, and accurate results, and it allows automatic probing that can be used to generate defect maps for further root cause analysis. The approach demonstrated in this paper shows the significant potential of EOTPR in soft failure characterization and in failure and reliability analysis.
for full paper see
https://dl.asminternational.org/istfa/proceedings/ISTFA2022/289/23926
Wednesday, 9 November 2022
Special Role of Mg2+ in the Formation of the Hydration Shell of Adenosine Triphosphate
Abstract
The hydration of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), Mg · ATP, and Ca · ATP in aqueous solutions has been analyzed based on the Terahertz Time-Domain Spectroscopy and Dynamic Light Scattering data. It is shown that the ATP binding with Mg2+ or Ca2+ leads to weakening of water binding in the hydration shell (apparently, due to the screening of the phosphate-group charge). It is also shown that an increased number of hydrogen bonds are formed in the hydration shells of Mg · ATP, which is not the case for ATP and Ca · ATP. The hydrodynamic diameter of Mg · ATP exceeds that of ATP and Ca · ATP, which is in agreement with the conclusion about the larger number of hydrogen bonds in the Mg · ATP hydration shell. The special role of Mg2+ in the ATP hydration may have a deep biological sense, because ATP is involved in most of biologically significant reactions specifically in the form of Mg · ATP complex.
for full paper see https://link.springer.com/article/10.3103/S1541308X22050090
… The spectra in the THz range were recorded on a TPS Spectra3000 (Teraview, UK) spectrometer. The THz-TDS method is known in detail; its description can be found, eg, in [29]. This method makes it possible to record simultaneously the …
Tuesday, 8 November 2022
Time of flight improved thermally grown oxide thickness measurement with terahertz spectroscopy
Zhang, Zhenghao, Yi Huang, Shuncong Zhong, Tingling Lin, Yujie Zhong, Qiuming Zeng, Walter Nsengiyumva, Yingjie Yu, and Zhike Peng. "Time of flight improved thermally grown oxide thickness measurement with terahertz spectroscopy." Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering 17, no. 4 (2022): 1-11.
for full paper see https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11465-022-0705-3
As a
nondestructive testing technique, terahertz time-domain spectroscopy technology
is commonly used to measure the thickness of ceramic coat in thermal barrier
coatings (TBCs). However, the invisibility of ceramic/thermally grown oxide
(TGO) reflective wave leads to the measurement failure of natural growth TGO
whose thickness is below 10 µm in TBCs. To detect and monitor TGO in the
emergence stage, a time of flight (TOF) improved TGO thickness measurement
method is proposed. A simulative investigation on propagation characteristics
of terahertz shows the linear relationship between TGO thickness and phase
shift of feature wave. The accurate TOF increment could be acquired from
wavelet soft threshold and cross-correlation function with negative effect
reduction of environmental noise and system oscillation. Thus, the TGO
thickness could be obtained efficiently from the TOF increment of the monitor
area with different heating times. The averaged error of 1.61 µm in
experimental results demonstrates the highly accurate and robust measurement of
the proposed method, making it attractive for condition monitoring and life
prediction of TBCs.
Monday, 25 July 2022
Single-particle and collective excitations of polar water molecules confined in nano-pores within a cordierite crystal lattice
Belyanchikov, M. A., Z. V. Bedran, M. Savinov, P. Bednyakov, P. Proschek, J. Prokleska, V. A. Abalmasov et al. "Single-particle and collective excitations of polar water molecules confined in nano-pores within a cordierite crystal lattice." Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 24, no. 11 (2022): 6890-6904.
Abstract
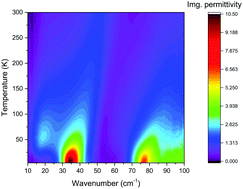
Recently, the low-temperature phase of water molecules confined within nanocages formed by the crystalline lattice of water-containing cordierite crystals has been reported to comprise domains with ferroelectrically ordered dipoles within the a, b-planes which are antiferroelectrically alternating along the c-axis. In the present work, comprehensive broad-band dielectric spectroscopy is combined with specific heat studies and molecular dynamics and Monte Carlo simulations in order to investigate in more detail the collective modes and single-particle excitations of nanoconfined water molecules. From DFT-MD simulations we reconstruct the potential-energy landscape experienced by the H2O molecules. A rich set of anisotropic temperature-dependent excitations is observed in the terahertz frequency range. Their origin is associated with the complex rotational/translational vibrations of confined H2O molecules. A strongly temperature dependent relaxational excitation, observed at radio-microwave frequencies for the electric field parallel to the crystallographic a-axis, E||a is analyzed in detail. The temperature dependences of loss-peak frequency and dielectric strength of the excitation together with specific heat data confirm a ferroelectric order–disorder phase transition at T0 ≈ 3 K in the network of H2O dipoles. Additional dielectric data are also provided for polarization E||b, too. Overall, these combined experimental investigations enable detailed conclusions concerning the dynamics of the confined water molecules that develop within their microscopic energy landscapes.
for full paper see
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2022/cp/d1cp05338h/unauth
… For terahertz measurements, a time-domain TeraView 3000
spectrometer was employed to directly determine the spectra of the real ε' and imaginary ε"
parts of the dielectric permittivity from the complex (amplitude and phase)
transmission …
Tuesday, 19 July 2022
Dispersive Spectrometry At Terahertz Frequencies for Probing the Quality of NbTiN Superconducting Films
Khudchenko, A., B. N. R. Lap, K. I. Rudakov, R. Hesper, V. P. Koshelets, P. N. Dmitriev, A. Chekushkin et al. "Dispersive Spectrometry At Terahertz Frequencies for Probing the Quality of NbTiN Superconducting Films." IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity 32, no. 4 (2022): 1-6.
Abstract:
Monday, 18 July 2022
Terahertz-infrared spectroscopy of wafer-scale films of single-walled carbon nanotubes treated by plasma
Zhukov, S. S., E. S. Zhukova, A. V. Melentev, B. P. Gorshunov, A. P. Tsapenko, D. S. Kopylova, and Albert G. Nasibulin. "Terahertz-infrared spectroscopy of wafer-scale films of single-walled carbon nanotubes treated by plasma." Carbon 189 (2022): 413-421.
Abstract
We investigated terahertz-infrared electrodynamic properties of wafer-scale films composed of plasma-treated single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) and films comprising SWCNTs grown with different lengths. The spectra of complex conductance of the films were measured at frequencies 5–20 000 cm−1 and in the temperature interval 5–300 K. Terahertz spectral response of films of pristine SWCNTs is well described with the Drude conductivity model and a plasmon resonance located at ≈100 cm−1. Stepwise treatment of the films with oxygen plasma led to a gradual suppression of the Drude spectral weight from the low-frequency side. For films with the nanotubes shorter than 1 μm, i.e., close to electrons mean free path and localization length, scattering of charge carriers at the nanotubes edges is shown to additionally contribute to the carriers scattering rate and to the damping of plasmon resonance. The temperature coefficient of ac resistance (ac TCR) in both kinds of films is found to strongly increase in amplitude during cooling and frequency decrease. The values of ac TCR increase in films with longer time of plasma treatment and nanotubes with shorter length but reach saturation in films with exposure time longer than ≈100 s or composed from SWCNTs shorter than 1 μm.
for full paper see
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0008622321012355
… For terahertz and infrared experiments commercial TeraView
time-domain spectrometer… complex (amplitude and phase) transmission coefficient measured with the TeraView
time-domain …
Tuesday, 21 June 2022
Polymer pellet fabrication for accurate THz-TDS measurements
Murphy, Keir N., Mira Naftaly, Alison Nordon, and Daniel Markl. "Polymer pellet fabrication for accurate THz-TDS measurements." Applied Sciences 12, no. 7 (2022): 3475.
for full paper see https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/12/7/3475/htm
Abstract
"2.2.3. THz-TDS Measurements
Monday, 20 June 2022
Detecting Crystallinity Using Terahertz Spectroscopy in 3D Printed Amorphous Solid Dispersions
Santitewagun, Supawan, Rishi Thakkar, J. Axel Zeitler, and Mohammed Maniruzzaman. "Detecting Crystallinity Using Terahertz Spectroscopy in 3D Printed Amorphous Solid Dispersions." Molecular Pharmaceutics (2022).
for full paper see https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.2c00163#
Abstract

This study demonstrates the applicability of terahertz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS) in evaluating the solid-state of the drug in selective laser sintering-based 3D printed dosage forms. Selective laser sintering is a powder bed-based 3D printing platform, which has recently demonstrated applicability in manufacturing amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs) through a layer-by-layer fusion process. When formulating ASDs, it is critical to confirm the final solid state of the drug as residual crystallinity can alter the performance of the formulation. Moreover, SLS 3D printing does not involve the mixing of the components during the process, which can lead to partially amorphous systems causing reproducibility and storage stability problems along with possibilities of unwanted polymorphism. In this study, a previously investigated SLS 3D printed ASD was characterized using THz-TDS and compared with traditionally used solid-state characterization techniques, including differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and powder X-ray diffractometry (pXRD). THz-TDS provided deeper insights into the solid state of the dosage forms and their properties. Moreover, THz-TDS was able to detect residual crystallinity in granules prepared using twin-screw granulation for the 3D printing process, which was undetectable by the DSC and XRD. THz-TDS can prove to be a useful tool in gaining deeper insights into the solid-state properties and further aid in predicting the stability of amorphous solid dispersions.
To learn more about terahertz applications visit www.teraview.com
Tuesday, 3 May 2022
Theoretical and experimental analysis of the dielectric properties of 3D orthogonal woven GFRP composites in the terahertz frequency range
A novel method to calculate the dielectric constant () of three-dimensional orthogonal woven glass fiber-reinforced polymer-matrix (3DOW-GFRP) composites in the terahertz (THz) frequency range is developed and experimentally verified using the THz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS). The dielectric anisotropy is demonstrated through simulation by considering a single propagation direction of the THz waves and three different fiber orientations in unidirectional GFRP composites. Simulation results are compared to those obtained from the classic rule-of-mixture equations to determine the representative equations for the three different cases of fiber orientations in the ()-coordinate system and a new model is developed to calculate of 3DOW-GFRP composites based on electromagnetic modeling principles. As opposed to previously reported lumped circuit models, our model addresses the issue of orthogonality of fiber and considers the shape and spatial disposition of the composite with respect to the polarization direction of the THz waves for accurate determination of . A comparison between the measured and calculated indicates that the proposed method is highly accurate with ≤ 2.68% maximum error, while the latter reaches 7.82% for the classic rule-of-mixture equations. This method is potentially useful for the design of 3DOW-GFRP with desired for applications such as electromagnetic shielding and electrostatic discharging structures.


